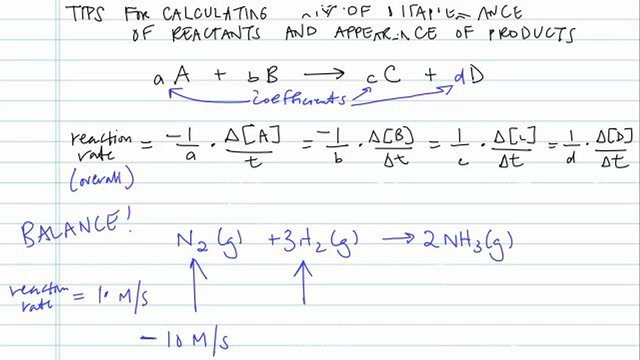
How to Calculate Initial Rate of Disappearance
Rate of disappearance of B rateΔBΔt. The rate of a chemical reaction is the change in concentration over the change in time.

Problem 14 6 Relating Rates Of Disappearance And Appearance Youtube
2HIg H2 g I2g The rate of disappearance of HI is twice that than the rate of appearance of H2.

. Rate of disappearance of B rateΔBΔt. Determining the Initial Rate from a Plot of Concentration Versus Time The initial rate of a reaction is the instantaneous rate at the start of the reaction ie when t 0. Rate of formation of C rateΔCΔt.
Rate of formation of D rateΔDΔt. Ce2NO Cl2 - 2NOCl The reaction is second order in ceNO and first order in ceCl2 and the initial rate equals pu143E-6 mol L-1 s-1 at the instant when ceNO_0 ceCl2_0 pu025 mol L-1. Rate of disappearance of A rateΔAΔt.
In the reaction betweem H2O2 and I- 15 mL of 030M KI 69. Using Figure 144 calculate the instantaneous rate of disappearance of C 4 H 9 Cl at t 0 the initial rate. 2 5 2 0.
In a series of experiments the following initial rates of disappearance of CO 2 were obtained. Calculate the rate of formation of ceNOCl. -Rate of appearance of product and disappearance of reactant is equal.
2O3 g 3O2 g Rate ΔO3 ΔO2 ----- -----. Because the rate remains the same when B is doubled the concentration of B has no effect on the reaction rate. 2 5 2.
The rate of a chemical reaction is the change in concentration over the change in time. Δ A will be negative as A will be lower at a later time since it is being used up in the reaction. For the hypothetical reaction A B calculate the average rate of disappearance of A if the initial concentration of A is 091 M and the concentration of A after 90 minutes is 011 M.
Calculate the intial rate of disappearance of H2O2 in units of M min-1 in 2 significant digits. However using this formula the rate of disappearance cannot be negative. Therefore the numerator in Δ A Δ t will be negative.
Calculate the average rate of disappearance of A if the initial concentration of A. 7 8 0. The rate law is therefore zero order in B that is n 0.
Rate of formation of C rateΔCΔt. The reaction rate can be defined thusly. Rate of disappearance is given as Δ A Δ t where A is a reactant.
DeltaBDeltat -030 Ms we just have to check the stoichiometry of the problem. The initial rate is equal to the negative of the slope of the curve of reactant concentration versus time at t 0. Then A final A initial will be negative.
ML of 010M H2O2 and 19 mL of 0020M Na2S2O3 were mixed in a flask containing starch and buffer and the total volume was made up to 500mL with distilled water. -Rate is then equal to 1Coeffcient minus change in concentration divided by. Rate kA2B0 kA2 Rate kA2 40 10 3 M 1 s 10050 M2 10 10 5 Ms.
Note that the overall rate of reaction is therefore 030 Ms. 7 8 M m i n. CO 2 H 2 Initial rate Ms.
The problem then says. Since twice as much A reacts with one equivalent of B its rate of disappearance is twice the rate of B think of it as A having to react. C Rate of disappearance K N O 2 C l 2 1 7 7.
Rate ΔHI ΔH2 ----- ----- 2 ΔT ΔT Example 1. The reaction rate can be defined thusly. How is the rate of disappearance of ozone related to the rate of appearance of oxygen in the following equation.
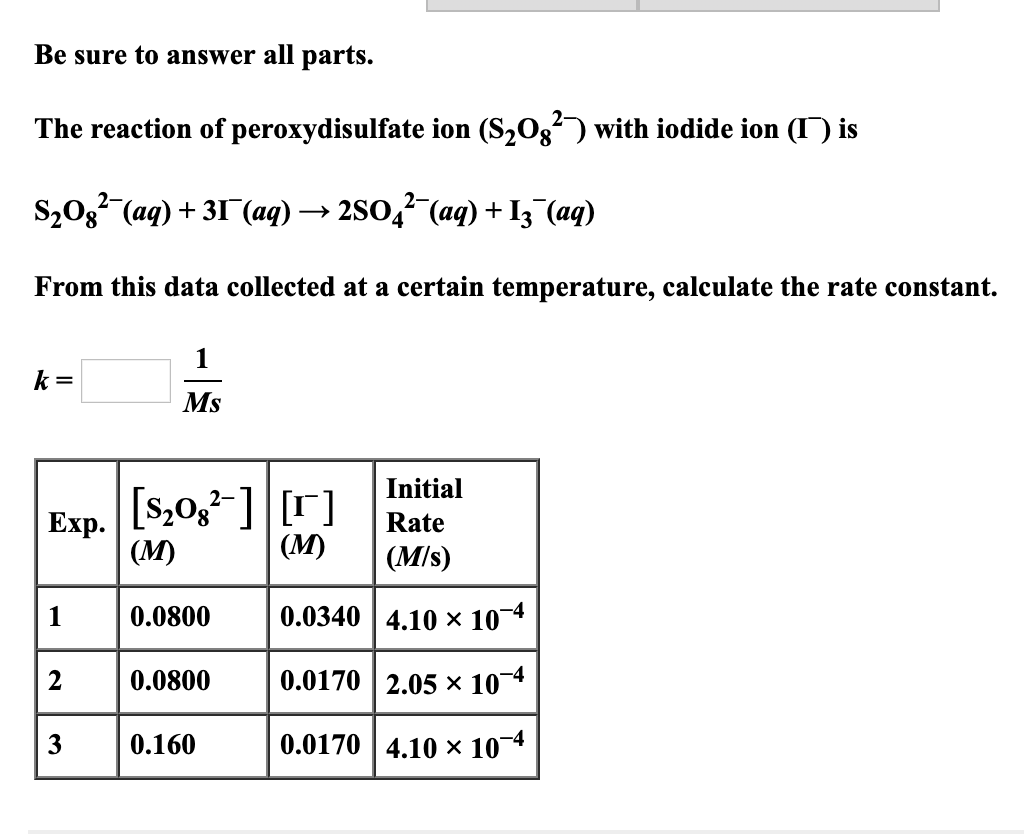
When Stoichiometry of Both Reactants and Products is equal. Rate of disappearance of A rateΔAΔt. Determine the rate law and calculate the value of the rate constant for this reaction.
What happens when there is nor 11 ratio. The following data are given for the reaction of ceNO text and ceCl2. For 2A B - 3C knowing that the rate of disappearance of B is 030 molLcdots ie.
Rates Of Disappearance And Appearance Concept Chemistry Video By Brightstorm
Solved Be Sure To Answer All Parts Consider The Reaction X Chegg Com

Problem 14 6 Relating Rates Of Disappearance And Appearance Youtube
No comments for "How to Calculate Initial Rate of Disappearance"
Post a Comment