Describe the Functional Histology of the Digestive Tract
Posterior to choanae and superior to soft palate. Mixed SMOOTH and SKELETAL muscle in the middle 13 of the esophagus.
Describe the peritoneum and mesenteries.
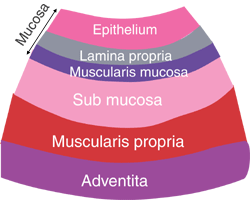
. Acts as passageway for both digestive esophagus and respiratory larynx system Divided into three regions. There is SMOOTH muscle in the lower 13 of the esophagus stomach duodenum jejunem ilium colon. Each layer has different tissues and functions.
Describe the functions of the digestive tract and explain how the digestive system works with other systems of the body to deliver important nutrients to body cells. There can be inner circular and outer longitudinal muscles. Explain the anatomy of the esophagus and stomach.
The secretions of the associated glandular organs such as the salivary glands pancreas liver and gall bladder aid the GI tract in accomplishing these functions. Except in the mouth esophagus and anus where its stratified squamous the epithelium of mucosa is a. 24-1 The Digestive Tract The Movement of Digestive Materials By muscular layers of digestive tract Consist of visceral smooth muscle tissue Along digestive tract Has rhythmic cycles of activity Controlled by pacesetter cells Cells undergo spontaneous depolarization Triggering wave of contraction through entire.
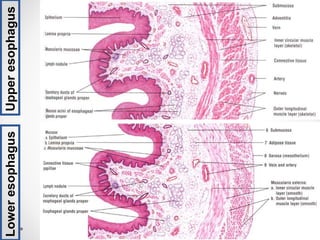
The mucosa is the innermost layer and functions in absorption and secretion. Histology Review Which part of the digestive tract is seen here. It prevents swallowed materials from entering the nasopharynx and nasal cavity.
After following this topic you should know how the structure of the stomach small and large intestine varies and how this is related to function the roles of the liver pancreas and gall bladder in. Notes DD DO Histology Review These tissue sections all show sections comes from the Panel 1 which tells you that all of these tissue Panel 2 Panel 3 Name the specific part of this organ shown in each panel and. The GI tract is composed of four layers.
Introduction to Digestive System. The innermost layer is the mucosa underneath this is the submucosa followed by the muscularis propria and finally the outermost layer - the adventitia. Describe the organ quadrant system and nine region system for dividing the abdominal cavity.
The GI tract is a muscular tube with a histological organization that is similar across all of its segments. Describe the functions of the digestive tract and explain how the digestive system works with other systems of the body to deliver important nutrients to body cells. Several distinct concentric layers line each segment of the tract.
Name the organs of the gastrointestinal tract versus the accessory organs that assist the GI tract. Chapter 23 Study Guide The Digestive System After reading and studying this chapter the successful student should be able to. 1 a lining epithelium 2 a lamina propria and 3 a musclularis mucosae.
Digestive mucosa is made up of three sublayers. The liver pancreas and gall bladder. Functions of the Digestive System We can regard digestive functions as a series of integrated steps.
Describe the anatomy of the small intestines and large. It is composed of epithelium cells and a thin connective tissue. The structural modifications of the different regions of the digestive tract reflect their functional specificity.
Analyze and describe the functions of the digestive system. Soft palate is an incomplete muscle and connective tissue partition that separates nasopharynx and oropharynx. 24 Learning Objective 24-1 j pgs 875-882 Identify the organs of the digestive system list their major functions describe the functional histology of the digestive tract and outline the mechanisms that regulate digestion.
Explain the histology of the GI tract wall. There is skeletal muscle in the oropharynx first 13 of the esophagus and the anus. The structure of these layers varies in different regions of the digestive system depending on their function.
Also includes the myenteric plexus Myenteric plexus a nerve plexus in between the inner circular layer and outer longitudinal layer of smooth muscle in the muscular propria. The digestive system can be broken down into two major components. Describe the histology of the.
List the 6 functions of the digestive system. This topic covers the structure and function of the stomach small and large intestines and other tissues important for digestion. The digestive system is responsible for the ingestion and digestion of dietary substances the absorption of nutrients and the elimination of waste products.
Transport food from pharynx to stomach. What feature did you use to identify it. O Ingestion occurs when materials enter the digestive tract via the mouth.
Layers of the Gastointestinal Tract. Mucosa submucosa muscularis and serosa. Namely mastication a sense of taste propulsion of foodstuffs digestion absorption and elimination.
O Mechanical processing is crushing and shearing that makes materials. The extramural digestive glands located outside the digestive tract deliver their. The mucosa surrounds the lumen of the GI tract and consists of an epithelial cell layer supported by a thin layer of connective tissue known as the lamina propria.
Ingestion is an active process involving conscious choice and decision making. Identify the major organs and accessory organs of the digestive tract Describe the basic functional histology of the digestive tract Explain the process by which materials move through the digestive tract Describe the anatomy and functions of the following regions of the digestive tract. Oral cavity pharynx and esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine.
Thick wall with 4 tunics sphincters at upper and lower end mucosa is moist stratified squamous epithelium. Describe the histology of the digestive tract including. There is the primary digestive tract which functions mainly as a conduit and storage pathwayThis portion is needed in order to move food contents along the tract peristalsis so that absorption of nutrients and excretion of undigested substances can occur.
Regulates the peristaltic contractions. The digestive tract consists of the mouth pharynx and digestive tube. From the inside out they are called.
This layer of the digestive tract consists of an inner circular and outer longitudinal layer of smooth muscle which cause peristalsis. Describe the function of that feature. The GI tract contains four layers.

Digestive Tract Growth And Differentiation In Shh Cre Fl Ihh Fl Download Scientific Diagram
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1841/PHU0MVO6zQp4UkEyCdSA_histology-of-stomach_low_mag_english.jpg)
No comments for "Describe the Functional Histology of the Digestive Tract"
Post a Comment